Version: 8.3.0
To create a Plane in the Main Menu select New Entity - > Basic - > Plane
There are three algorithms to create a plane in the 3D space.
The Result of each operation will be a GEOM_Object (face).
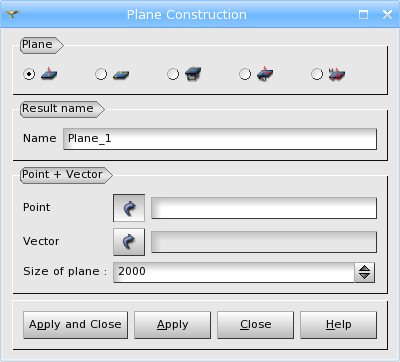
Firstly, you can define a Plane by a Point through which the plane passes, a Vector giving a normal of the plane and a Size of the Plane (size of a side of quadrangle face, representing the plane).
TUI Command: geompy.MakePlane(Point, Vector, TrimSize)
Arguments: Name + 1 vertex + 1 vector + 1 value (to define the size of the plane).
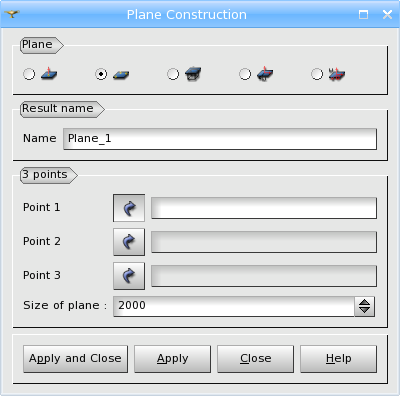
Secondly, you can define a Plane by three Points through which the plane passes and a Size of the Plane.
TUI Command: geompy.MakePlaneThreePnt(Point1, Point2, Point3, TrimSize)
Arguments: Name + 3 vertices + 1 value (to define the size of the plane).
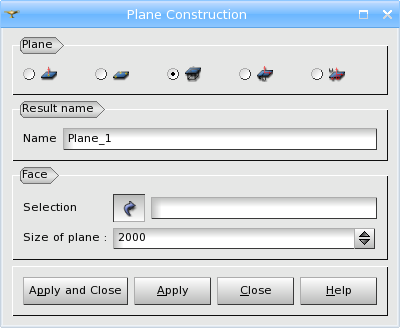
Thirdly, you can define a Plane by another Plane or Face and a Size of the Plane.
TUI Command: geompy.MakePlaneFace(Face, TrimSize)
Arguments: Name + 1 face + 1 value (to define the size of the plane).
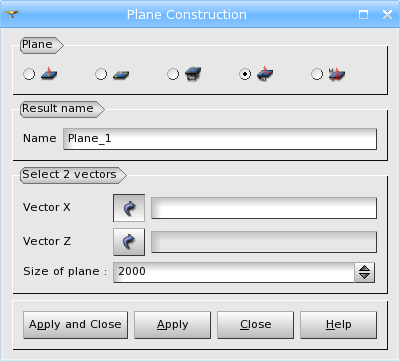
Fourthly, you can define a Plane by two Vectors. The first vector defines the center point and the direction, the second vector defines the normal to the Plane.
TUI Command: geompy.MakePlane2Vec(Vec1, Vec2, TrimSize)
Arguments: Name + 2 vectors + 1 value (to define the size of the plane).
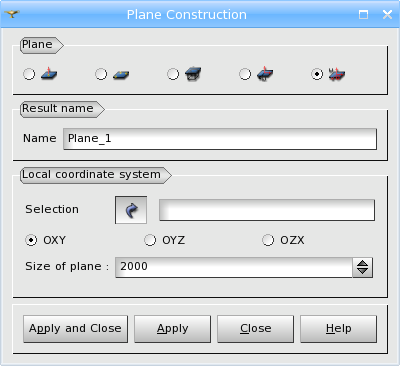
Finally, you can define a Plane by the Local Coordinate System and the orientation (OXY, OYZ, OZX).
TUI Command: geompy.MakePlaneLCS(LCS, TrimSize, [1, 2, or 3])
Arguments: Name + LCS + 1 value (to define the size of the plane) + 1 value (to define the orientation)
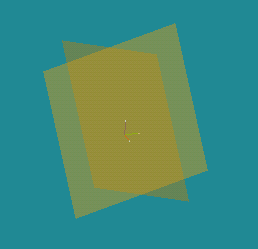
Examples:
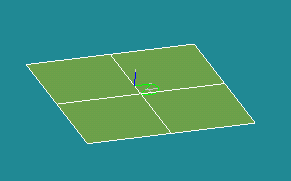
Our TUI Scripts provide you with useful examples of creation of Basic Geometric Objects.