Version: 8.3.0
Sewing operation allows uniting several faces (possibly contained in a shell, solid or compound) into one shell. Geometrically coincident (within a specified tolerance) edges (or parts of edges) of different faces are replaced by one edge thus producing a shell of faces with shared boundaries.
This operation is similar to New Entity - > Build - > Shell operation, the difference is that with Sewing you can specify the tolerance and get a non-manifold result.
The possibility to create a non-manifold shell can be used e.g. to create a shell forming several closed domains and then to create several solids with shared boundaries from this shell.
To produce a Sewing operation in the Main Menu select Repair - > Sewing.
The Result will be a GEOM_Object (shell).
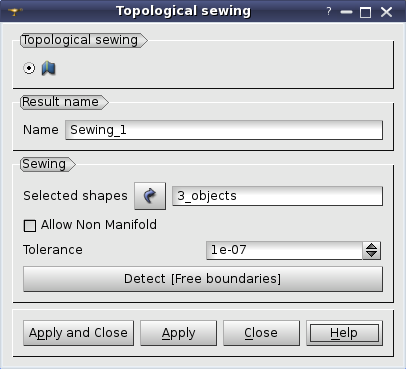
In this dialog:
This operation can be also launched using a TUI Command:
geompy.MakeSewing(ListOfShape, Precision, AllowNonManifold=False),
where ListOfShape is a list of faces or shells to be sewn, Precision is a precision for sewing, AllowNonManifold is a flag that allows non-manifold sewing.
Example:


Our TUI Scripts provide you with useful examples of the use of Repairing Operations.