Version: 8.3.0
It is frequently asked about the difference between the above mentioned operations. It is indeed simple. Let us take the example of a cylinder and a box that you want to join together.
The fuse operation will make a single solid from two given solids. It allows you to build complex models by putting simple shapes together.
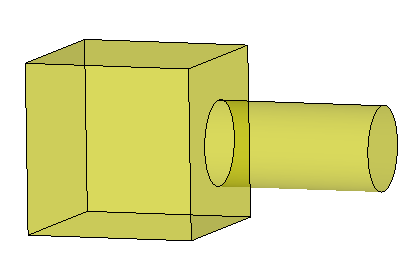
The partition operation will also connect the solids but it will keep a face at the frontier (in brown in the picture below). The resulting shape will consist of two connected solids that share a face at their frontier. It means that this face is present only one time in the resulting shape and is a sub-shape of both the box and the cylinder.
This operation allows you to identify different areas in a shape (e.g. different materials) and to ensure a conformal mesh when meshing it later. Indeed the face at the frontier is meshed only once.
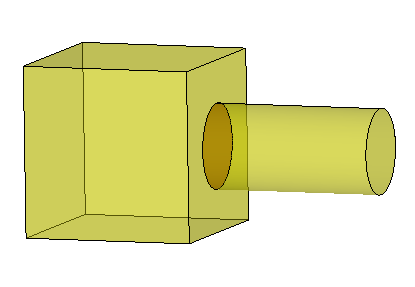
When you build a compound by using the Build -> Compound operation you just make an object that contains two separate solids like in a "bag". The two solids remain unconnected. The compound is just a set of shapes, no more.
The compound allows applying operations to a collection of shapes.
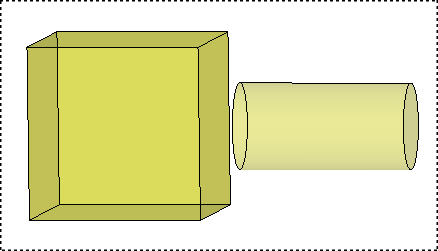
In the frame of this example we can summarize the following differences: