- Objectives
- Principles
- A complete example
- How to select an object of the object browser
- Other examples
Objectives
The SALOME python plugin manager allows the end user to extend the graphic interface of SALOME with custom functions written as python modules. The screenshots below show the example of a tool that creates a mesh from a set of geometrical parameters with the support of simple graphical interface:
The default menu for plugins is "Tool->Extensions":
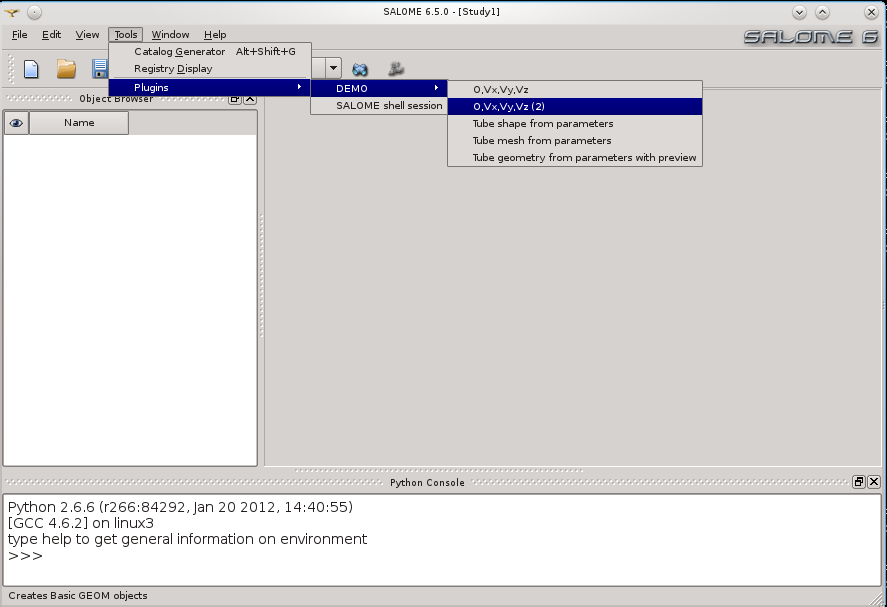
In this example, the plugin provides a small interface to input the parameters (not provided by the plugin manager):
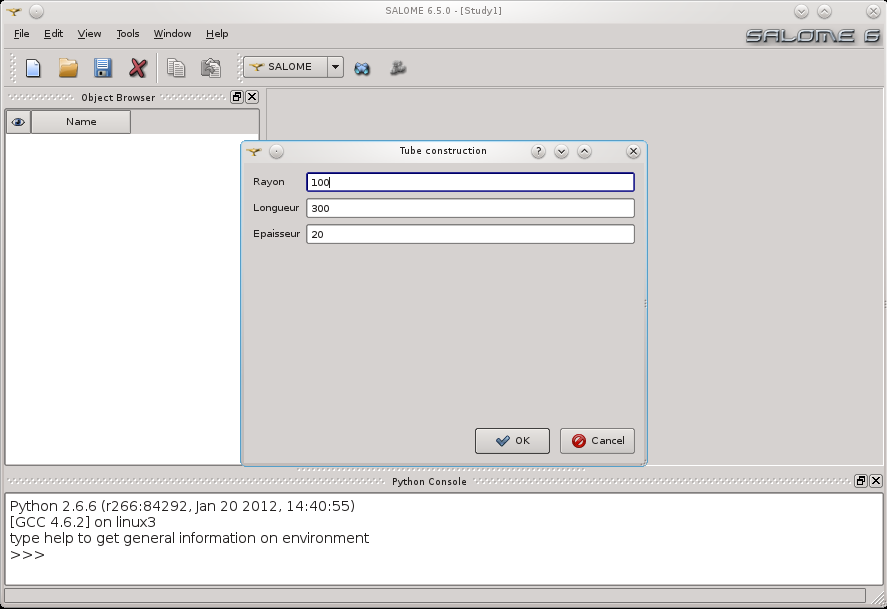
Then creates the mesh model:
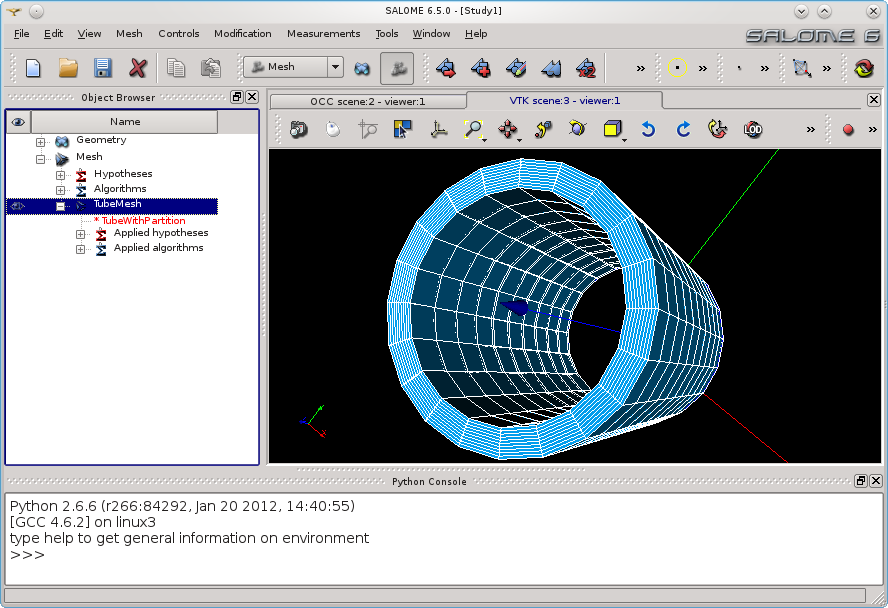
In this example, the end user has to write:
- the python script that creates the mesh from the parameters, using the GEOM and SMESH python interface, as in a classic use case,
- the dialog box in PyQt to input the parameters,
- the file salome_plugins.py that declares the plugins.
This page explains only the last point.
Principles
The general form of the file salome_plugins.py is:
The procedure is to define a function that implements the plugin, and to declare this function to the plugins manager. The implementation can be very variable. It is advisable to consider this function as a proxy to your code that you can manage in a python package installed in the standard SALOME python directories.
In this code, the variable "context" is automatically transmitted by the pluginmanager when you request the plugin. This context provides you with at least the following attributes:
Once written, this script salome_plugin.py has to be moved to a specific place on your filesystem where SALOME is programmed to search for plugins. The possible directories are (in search order):
- The directory <*_ROOT_DIR>/share/salome/plugins/<module_name>, when this plugin is developped in the framework of a SALOME module (<*_ROOT_DIR> is the root installation directory of the module, and <module_name> is the name of the module in low letters).
- The directory ~/.config/salome/Plugins for personnal end user plugins.
- Any path in the shell variable SALOME_PLUGINS_PATH (each path must be separated by a comma ":" for unix and ";" for windows). This variable should be set and exported before running the SALOME application.
A complete example
Suppose that you write a SALOME script that creates a trihedron for each of your studies (a simple and standard SALOME script, that every end user is capable to write if he reads the documentation and follows the training course):
The job consists in creating the file salome_plugins.py as follows:
Move this script in the directory ~/.config/salome/Plugins, run SALOME and enjoy your new function.
How to select an object of the object browser
Sometimes it can be useful to retrieve an object of the object browser to perform an action on it, for example, to select a mesh and display some information related to it.
Some important methods and objects to use are as follows:
- context.sg.getObjectBrowser(): to connect the signal event
selectionChanged()to a custom slot - context.salome.sg.getAllSelected(): to get the list of selected object in the object browser
- objId = context.salome.sg.getSelected(0): to get the first selected object in the object browser
salomeObj = context.salome.study.FindObjectID(objId).GetObject(): to retrieve the salome object from selection. It can be a GEOM, SMESH, or any other module object.
If it is a mesh, then it is possible to call methods of the SMESH::SMESH_Mesh interface on the object, for example GetShapeToMesh(). If it is not a mesh, this call will raise an exception. So it is possible to write the code retrieving the shape a mesh is built on in the following way:
mesh = Nonetry:shape = salomeObj.GetShapeToMesh()except:print "The selection is not a mesh"
An example of those methods is available with the demo examples. See the next chapter Other examples.
Other examples
The GUI module provides you with some basic demo examples located in the directory src/SalomeApp/pluginsdemo of the source space and installed in the directory $GUI_ROOT_DIR/share/salome/plugins/gui/demo.
- Note
- These examples are automatically installed when you install the GUI but are not activated. To activate the plugins, edit the file $GUI_ROOT_DIR/share/salome/plugins/gui/demo/salome_plugins.py and turn the variable DEMO_IS_ACTIVATED to True.
The demo examples are:
- trihedron: create a trihedron and display it with fit on the size
- tube_shapewithgui: create a geom object from parameters given by a dialog box.
- tube_meshwithgui: create a mesh object from parameters given by a dialog box. This illustrates that a plugin can work with more than one SALOME module.
- tube_shapewithguiAndPreview: same than tube_shapewithgui but with an additionnal preview function (button apply in the dialog box).
- runSalomeShellSession: run a SALOME prepared shell session in a xterm.
- minmax: computes the min and max values of a control on a selected mesh.
- Note
- This plugin is available in the SMESH module only. To activate it, edit the file $GUI_ROOT_DIR/share/salome/plugins/gui/demo/smesh_plugins.py and turn the variable DEMO_IS_ACTIVATED to True.