Version: 8.3.0
MG-Tetra Parameters hypothesis works only with MG-Tetra meshing algorithm which uses MG-Tetra_HPC code (formerly tepal) which is the parallel implementation of MG-Tetra (formerly TetMesh-GHS3D) algorithm. This algorithm is a DISTENE commercial software, its use requires a license.
See http://www.distene.com and http://www.meshgems.com/volume-meshing-meshgems-tetra.html.
MG-Tetra-hpc (Tepal V3 in fact) gives the possibility to generate a partitioned mesh with more than 200 million tetrahedrons on computers using MPI. The launch of this version is described below.
This is a serious alternative to MG-Tetra, which requires a much less common configuration with 64Go RAM to only try to make a partition of a mesh with 200 million tetrahedrons, no result guaranteed (in 2010).
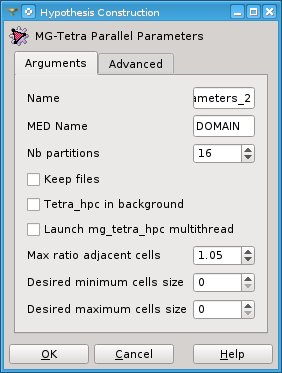
Discard subdomains - if this box is checked, discard the parallel sub-domains (mesh, global numbering and interfaces).
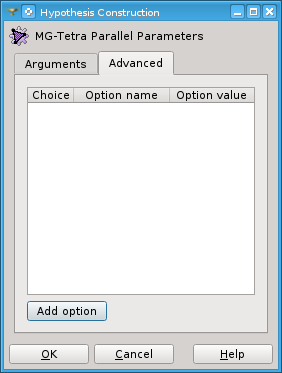
In Advanced tab page you can specify not exposed options of MG_Tetra-hpc.
Add option adds a line to the table where you can type an option and its value as text. A check box in the first column activates/deactivates the option of the current row. A deactivated option will be erased upon pressing Ok.
MG-Tetra_HPC plug-in launches a standalone binary executable tetrahpc2med.
tetrahpc2med launches MG_Tetra-hpc, waits for the end of computation, and converts the resulting output files into MED files.
Some advanced optional parameters are accessible as arguments.
If Keep Files option is checked, it is possible to re-launch tetrahpc2med or MG-Tetra-hpc in the Terminal as a command with custom parameters.
Advanced tetrahpc2med Parameters - type tetrahpc2med –help in the Terminal.
myname@myhost > /export/home/myname/salome_7/GHS3DPRLPLUGIN/bin/salome/tetrahpc2med --help
tetrahpc2med V3.0 (MED3+tetra-hpc) Available options:
--help : produces this help message
--casename : path and name of input tetrahpc2med files which are
- output files of GHS3DPRL_Plugin .mesh
- output file of GHS3DPRL_Plugin casename_skin.med (optional)
with initial skin and its initial groups
--number : number of partitions
--medname : path and name of output MED files
--limitswap : max size of working cpu memory (Mo) (before swapping on .temp files)
--verbose : trace of execution (0->6)
--test : more tests about joints, before generation of output files
--menu : a GUI menu for option number
--launchtetra : also launch tetra-hpc on files casename.mesh and option number
--merge_subdomains : merge the subdomains into one mesh and write the output .mesh(b) file
--tag_subdomains : use the parallel subdomain index as tag into the merged output mesh
to identify the parallel subdomains (used in combination with the merge_subdomains option)
--output_interfaces : write the parallel subdomains interface triangles into the merged output mesh
(used in combination with the merge_subdomains option)
--discard_subdomains : discard the parallel subdomains informations output (mesh, global numbering and interfaces)
--background : force background mode from launch tetra-hpc and generation of final MED files (big meshes)
--deletegroups : regular expression (see QRegExp) which matches unwanted groups in final MED files
(try --deletegroups="(\bJOINT)"
(try --deletegroups="(\bAll_Nodes|\bAll_Faces)"
(try --deletegroups="((\bAll_|\bNew_)(N|F|T))"
example:
tetrahpc2med --casename=/tmp/GHS3DPRL --number=2 --medname=DOMAIN --limitswap=1000 --verbose=0 --test=yes --menu=no --launchtetra=no
Advanced tetra_hpc parameters (2014)
Usage: tetra_hpc.exe [options]
Options:
Short option (if it exists)
/ Long option
| / Description
| | /
v v v
--help
print this help
--in <input mesh file name>
Sets the input file
(MANDATORY)
--out <output mesh file name>
Sets the output file
(MANDATORY)
--merge_subdomains <merge>
Describes whether to merge the subdomains into one mesh and write the
output .mesh(b) file or not.
if <merge> is
yes : the subdomains will be merged into one mesh and written to
the output .mesh(b),
no : the subdomains will not be merged.
default : no
--tag_subdomains <tag>
Describes whether to use the parallel subdomain index as tag into the
merged output mesh or not (used in combination with the
merge_subdomains option).
if <tag> is
yes : the tags of the tetrahedra in the merged output will
identify the parallel subdomains,
no : the tag will keep its standard meaning of volume domain.
default : no
--output_interfaces <output_interfaces>
Describes whether to write the parallel subdomains interface
triangles into the merged output mesh or not (used in combination
with the merge_subdomains option).
if <output_interfaces> is
yes : the parallel subdomains interface triangles will be written
into the merged output mesh,
no : they will not be added to the merged output mesh.
default : no
--verbose <verbose>
Set the verbosity level, increasing from 0 to 10.
<verbose> values are increasing from 0 to 10 :
0 : no details
10 : very detailed
default : 3
--discard_subdomains <discard>
Describes whether to discard the parallel subdomains (mesh, global
numbering and interfaces) or not.
if <discard> is
yes : the subdomain informations (mesh, global numbering and
interfaces) will be discarded,
no : they will be written to disk as output.
default : no
MG-Tetra_HPC plug-in launches standalone binary executable tetrahpc2med.
You may rename file tetrahpc2med as tetrahpc2med.exe for example, and replace tetrahpc2med by a shell script at your convenience to overriding parameters.
... or else $PATH modification... .
Advanced tetrahpc2med Parameters - overriding parameter deletegroups
You may rename tetrahpc2med as tetrahpc2med.exe for example.
This 2014 beta-version needs MPI, (openmpi was used). To use it you have to proceed as below.
Obsolete example tepal_v2_mpirun.
example ex30_tepal.py.