The schema YACS¶
The object YACS contains every definition that allows the creation of a schema. This schema will drive the alternation of the computation of a physical modelization over a mesh and the adaptation of the mesh for the computation. This alternation is driven by some criteria for the convergence.
Note
To read an exhaustive description of any part of the schema, see YACS
Procedure¶
The automatic creation of the schema is going to be made in three phases.
- At first, it is necessary to have done a calculation on the very first mesh. This calculation will have produced the results in a MED file.
- Then, a case is created in the module HOMARD, as described in The creation of a case. In this case, we create the following iteration of the mesh by defining a hypothesis of adaptation ; see The iteration.
- Last, from this case, a schema will be created, based on the hypothesis for the adaptation.
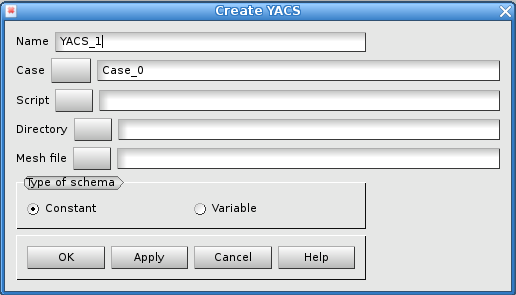
Name of the schema¶
A name of schema is automatically proposed: YACS_1, YACS_2, etc. This name can be modified. He must not have been already used for another schema.
The script¶
The file containing the script which allows to launch the calculation connected to the physical modelling is supplied here. It is a script python who has to respect the following rules:
- the name of the class which manages the calculation is Script
- to launch the calculation is made by the method``Compute()``
- the result of the calculation is under the shape of three variables: the code of error, a message, a dictionary python.
If they are necessary for the creation of the class, we can supply arguments under the shape:
- --rep_calc=rep_calc, where rep_calc is the directory for the computation
- --num=num, where num eis the number of calculation : 0 for the very first calculation, then 1, 2 etc.
- --mesh_file=meshfile, where meshfile is the file that contains the mesh for the computation
- -v, for the messages
In return:
- error : the error code, integer: 0 if it was correct, non 0 if not
- message : a possible message of information about the calculation
- dico_resu : a dictionary python that contains at less the two following keys: FileName is the key for the name of the MED file which contains the results of the calculation, V_TEST is the key for the real value to be tested.
Example for the script:
argu = ["--rep_calc=" + rep_calc)]
argu.append("--num=%d" % numCalc)
argu.append("--mesh_file=" + MeshFile)
Script_A = Script(argu)
error, message, dico_resu = Script_A.compute ()
The directory¶
The directory will countain all the files producted by the computations. By default, nothing is suggested. The choice is made either by giving a name into the text zone or by a selection through the search window.
The initial mesh¶
The initial mesh must be stored into a MED file. It is the very first mesh that is used to solve the physical problem. The name of the file is choosen either by giving a name into the text zone or by a selection through the search window.
The type of the schema¶
Two types of schemas are proposed: constant or variable.
The default choice, ‘constant’, alternate a computation that is always the same and a mesh adaptation: from a computation to another one, the only part that is changed is the mesh. All the rest is identical. For example, in case the calculation would model a transient phenomenon, it is always the completeness of the transient phenomenon that is taken into account.
The option ‘variable’ is inactive today.
Saving the schema¶
By default, the schema is saved into the file schema.xml in the directory of the case that is under the schema. If the file is deleted, it can be rewritten by the mouse option Write.
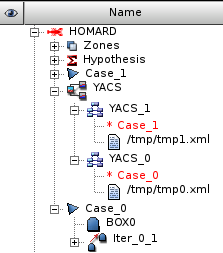
Object browser¶
The object browser contains the created schemas, identified by their names. They can be edited. Under every schema, there is a link to the case and the reference to the xml file that is written. This file can be read.
Corresponding python functions¶
Look The schema YACS
How to use the schema¶
The schema that is produced by this procedure can be imported into the module YACS. It can be executed without any modification. It this case, the stop into the loop is done:
- either the maximal number of iterations for the loop (calcul,adaptation) is reached;
- or the test for the convergence over the variable V_TEST is satisfied.
By default, the maximal number of iterations is equal to 5 and the test for the convergence is satisfied if the variable varies less than one per a thousand in a relative value, between two successive iterations. These tests can be modified.
These tests ares done into the node “Analyse” of the schema, as described in YACS.
The maximal number of iterations is given by the variable NbCalcMax:
NbCalcMax = 5
The value for the test is saved in a list all along the calculations:
valeur_v = dico_resu["V_TEST"]
if NumCalc == 0 :
resu1 = [valeur_v]
else :
resu1.append(valeur_v)
and the test is calculated after the second iteration:
solu_m1 = resu1[-2]
rap = ( resu1[-1] - solu_m1 ) / solu_m1
if abs(rap) < 0.001 :
MessInfo = ""
Error = -9999
break
If this test is modified, it must be done here. But the instructions when it is converged must be kept to guarantee a good execution:
MessInfo = ""
Error = -9999
break
Examples¶
A user’s guide for schemas with Code_Aster is available here: A schema YACS for Code_Aster.