| Version 20 (modified by , 13 years ago) (diff) |
|---|
Visualization with OpenGL hands-on
Tutorial aims to introduce visualization techniques with modern Open Graphics Language (OpenGL) approaches standardized with version 3.x+. OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL) is used for that without tendency to introduce photo-realismas output but rather useful colors for scientific data exploration.
Running this tutorial on Linux desktop one requires at least the OpenGL 2.0 graphics with the GLSL 1.1 and supporting libraries GL, GLU, GLUT, GLEW. This can be verified with the following commands:
$ glxinfo |grep OpenGL.*version OpenGL version string: 2.1 Mesa 8.0.5 OpenGL shading language version string: 1.20 $ ls /usr/include/GL/{glut.h,glew.h,gl.h,glu.h} /usr/include/GL/glew.h /usr/include/GL/glu.h /usr/include/GL/gl.h /usr/include/GL/glut.h
Legacy OpenGL
Create the following first.c using your favorite editor.
#include <GL/glut.h> void display() { glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); glColor3f(1.0, 0.4, 1.0); glBegin(GL_LINES); glVertex2f(0.1, 0.1); glVertex3f(0.8, 0.8, 1.0); glEnd(); glutSwapBuffers(); } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { glutInit(&argc,argv); glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_DOUBLE); glutCreateWindow("first.c GL code"); glutDisplayFunc(display); glutMainLoop(); return 0; }
Create Makefile to build your program. 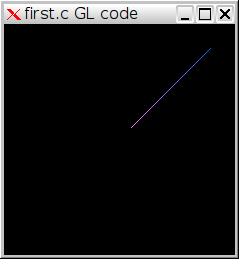
CFLAGS=-Wall LDFLAGS=-lGL -lGLU -lglut -lGLEW ALL=first default: $(ALL) first : first.o clean: rm -rf *~ *.o $(ALL)
Beware that Makefile is TAB aware. So the last line should contain TAB indentation and not spacing.
Make and run the program with
make ./first
Try the same program in Python
from OpenGL.GLUT import * from OpenGL.GL import * import sys def display(): glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT) glColor3f(1.0, 0.4, 1.0) glBegin(GL_LINES) glVertex2f(0.1, 0.1) glVertex3f(0.8, 0.8, 1.0) glEnd() glutSwapBuffers() if __name__ == "__main__": glutInit(sys.argv) glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_DOUBLE) glutCreateWindow("first.py GL code") glutDisplayFunc(display) glutMainLoop()
and run it with
python first.py
Exercises #1:
- Add RGB color to vertices with
glColor3f(0.0, 0.4, 1.0);. - Replace single line drawing in
display()with the following snippetand try to draw two wireframe triangles in a loop. Change primitive toGLfloat vertices[][2] = { { -0.90, -0.90 }, // Triangle 1 { 0.85, -0.90 }, { -0.90, 0.85 }, { 0.90, -0.85 }, // Triangle 2 { 0.90, 0.90 }, { -0.85, 0.90 } };
GL_LINE_LOOP. - Draw two primitives with
GL_TRIANGLES.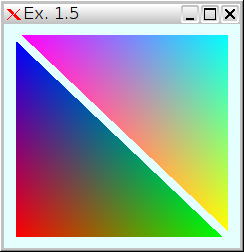
- Add different color to each vertex.
GLfloat color[][3] = { {1, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 0}, {0, 1, 1}, {1, 0, 1}};
- Replace loop with the following
How can we add color to vertices? See glColorPointer and glEnableClientState.
glVertexPointer(2, GL_FLOAT, 0, &vertices[0][0]); glEnableClientState(GL_VERTEX_ARRAY); glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 6); glDisableClientState(GL_VERTEX_ARRAY);
- Change background to
glClearColor(0.9,1,1,1.0);and suggest initial window inmain()glutInitWindowSize(512, 512); glutInitWindowPosition((glutGet(GLUT_SCREEN_WIDTH)-512)/2, (glutGet(GLUT_SCREEN_HEIGHT)-512)/2);
- Add keyboard event
to quit the program when pressing ESCape key with keycode 27 by adding callback function
and registering event within
void keyboard(unsigned char key, int x, int y) { if (key == 27) exit(0); }
main()byglutKeyboardFunc(keyboard);. Some preferkey == 'q', though.
Modern OpenGL
We extend previous exercise with example that introduces OpenGL 3.x techniques:
- OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL 1.2) where simple vertex and fragment shader are required.
- Vertex Aray Objects (VAOs) and vertex buffers (VBOs) stored in GPU.
Create triangle.c and update Makefile with new target
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <GL/glew.h> #include <GL/glut.h> static const GLchar * vertex_shader[] = {"void main()" "{" " gl_Position = ftransform();" "}" }; static const GLchar * fragment_shader[] = {"void main()" "{" " gl_FragColor = vec4(0.4,0.4,0.8,1.0);" "}" }; void setShaders() { GLuint v, f, p; v = glCreateShader(GL_VERTEX_SHADER); f = glCreateShader(GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER); glShaderSource(v, 1, vertex_shader, NULL); glShaderSource(f, 1, fragment_shader, NULL); glCompileShader(v); glCompileShader(f); p = glCreateProgram(); glAttachShader(p,f); glAttachShader(p,v); glLinkProgram(p); glUseProgram(p); } enum VAO_IDs { Triangles, NumVAOs }; enum Buffer_IDs {ArrayBuffer,NumBuffers}; enum Attrib_IDs { vPosition = 0 }; GLuint VAOs[NumVAOs]; GLuint Buffers[NumBuffers]; #define NumVertices 6 void init(void) { glGenVertexArrays(NumVAOs, VAOs); glBindVertexArray(VAOs[Triangles]); GLfloat vertices[NumVertices][2] = { { -0.90, -0.90 }, // Triangle 1 { 0.85, -0.90 }, { -0.90, 0.85 }, { 0.90, -0.85 }, // Triangle 2 { 0.90, 0.90 }, { -0.85, 0.90 } }; glGenBuffers(NumBuffers, Buffers); glBindBuffer( GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, Buffers[ArrayBuffer]); glBufferData( GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertices), vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW); glVertexAttribPointer(vPosition, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, (const void*)0); glEnableVertexAttribArray(vPosition); } void display(void) { glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); glBindVertexArray(VAOs[Triangles]); glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, NumVertices); glutSwapBuffers(); } int main(int argc, char **argv) { glutInit(&argc, argv); glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_RGBA | GLUT_DOUBLE); glutCreateWindow("GLSL Intro"); glutDisplayFunc(display); glewInit(); if (!glewIsSupported("GL_VERSION_2_0")) { printf("GLSL not supported\n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } glClearColor(0.9,1.0,1.0,1.0); init(); setShaders(); glutMainLoop(); return 0; }
Exercises #2
- To be able to continue and not get lost introduce shader compiler logs in case of compilation errors by adding the following code into
setShaders()right at after vertex shader compilation:Do not forget to repeat the same thing for fragment shader. Add linker debuggingGLint compiled; glGetShaderiv(v, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &compiled ); if ( !compiled ) { GLsizei len; glGetShaderiv( v, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &len ); GLchar* log = malloc(sizeof(GLchar)*(len+1)); printf("Vertex Shader compilation failed: %s\n", log); free(log); }
Create some error to verify if it works. For general (core) OpenGL errors we can use the followingGLint linked; glGetProgramiv(p, GL_LINK_STATUS, &linked ); if ( !linked ) { GLsizei len; glGetProgramiv( p, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &len ); GLchar* log = malloc(sizeof(GLchar)*(len+1)); glGetProgramInfoLog( p, len, &len, log ); printf("Shader linking failed: %s\n", log); free(log); }
glcheck()utility at suspicious places.#define glcheck() {GLenum s; if ((s=glGetError()) != GL_NO_ERROR) \ fprintf (stderr, "OpenGL Error: %s at line %d\n", \ gluErrorString(s), __LINE__);} - Introduce vertex temperature with additional array and buffer at the end off
init()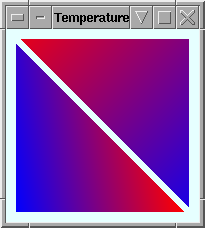 and adding corresponding IDs to
and adding corresponding IDs toGLfloat vertex_temperature[] = {0, 1, 0.2, 0.1, 0.5, 0.9}; glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, Buffers[TempBuffer]); glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertex_temperature), vertex_temperature, GL_STATIC_DRAW); glVertexAttribPointer(tPosition, 1, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, NULL); glEnableVertexAttribArray(tPosition);//toggle this
VAOsand buffers. Replace shaders withWhat happens if we don't enable temperature vertex array? Confer temperature.c attached if having troubles.static const GLchar * vertex_shader[] = { "" "attribute float temperature;" // custom variable along with vertex position "varying float t;" // communicate between the vertex and the fragment shader "void main()" "{" " t = temperature;" " gl_Position = gl_ModelViewProjectionMatrix * gl_Vertex;" "}" }; static const GLchar * fragment_shader[] = { "vec3 Cool = vec3(0, 0, 1);" // Red "vec3 Hot = vec3(1, 0, 0);" // Blue "varying float t;" // Interpolated by fragment "void main()" "{" " vec3 color = mix(Cool, Hot, t);" // use the built-in mix() function " gl_FragColor = vec4(color, 1.0);" // append alpha channel "}" };
- Add additional custom vertex array for the pressure. Change the temperature array to have values in Celsius for water boiling range [0-100]°C. Pressure should be in the range of [0-1] MPa. Scaling to color range [0-1] should be done in shaders. Toggle between them with the keyboard event by using the keys
'p'and't' thatglEnableVertexAttribArray()andglDisableVertexAttribArray()corresponding vertex attribute arrays.
Interactivity
Assemble the following Utah teapot model and attached virtual trackball.h and trackball.c sources from SGI. We use
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <GL/glew.h> #include <GL/glut.h> #include "trackball.h" GLuint p; // program needs to be global! float lpos[4] = {1, 0.5, 1, 0}; GLfloat m[4][4]; // modelview rotation matrix float last[4], cur[4]; // rotation tracking quaternions int width, height, beginx, beginy; float p1x, p1y, p2x, p2y; void display(void) { GLuint location = glGetUniformLocation(p, "RotationMatrix"); build_rotmatrix(m, cur); glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); glLightfv(GL_LIGHT0, GL_POSITION, lpos); if( location >= 0 ) glUniformMatrix4fv(location, 1, GL_FALSE, &m[0][0]); glutSolidTeapot(0.6); glutSwapBuffers(); } void processNormalKeys(unsigned char key, int x, int y) { if (key == 27) exit(0); } void mouse(int button,int state, int x, int y) { beginx = x; beginy = y; } void motion(int x,int y) { p1x = (2.0*beginx - width)/width; p1y = (height - 2.0*beginy)/height; p2x = (2.0 * x - width) / width; p2y = (height - 2.0 * y) / height; trackball(last, p1x, p1y, p2x, p2y); add_quats(last, cur, cur); beginx = x; beginy = y; glutPostRedisplay(); } void reshape (int w, int h) { double l = 1; width=w; height=h; glViewport (0, 0, w, h); glMatrixMode (GL_PROJECTION); glLoadIdentity(); glOrtho(-l, l, -l, l, -l, l); glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW); glLoadIdentity(); } static const GLchar * vertex_shader[] ={"\ varying vec3 normal, lightDir;\ uniform mat4 RotationMatrix;\ void main()\ { \ lightDir=normalize(vec3(gl_LightSource[0].position));\ normal=normalize(gl_NormalMatrix*gl_Normal);\ gl_Position = gl_ProjectionMatrix * \ RotationMatrix*gl_ModelViewMatrix*gl_Vertex;\ }"}; static const GLchar * fragment_shader[] ={"\ /* simple toon fragment shader */\ /* www.lighthouse3d.com */\ \ varying vec3 normal, lightDir;\ \ void main()\ {\ float intensity;\ vec3 n;\ vec4 color;\ \ n = normalize(normal);\ intensity = max(dot(lightDir,n),0.0);\ if (intensity > 0.98)\ color = vec4(0.8,0.8,0.8,1.0);\ else if (intensity > 0.5)\ color = vec4(0.4,0.4,0.8,1.0);\ else if (intensity > 0.25)\ color = vec4(0.2,0.2,0.4,1.0);\ else\ color = vec4(0.1,0.1,0.1,1.0);\ gl_FragColor = color;\ }"}; void setShaders() { GLuint v, f; v = glCreateShader(GL_VERTEX_SHADER); f = glCreateShader(GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER); glShaderSource(v, 1, vertex_shader, NULL); glShaderSource(f, 1, fragment_shader, NULL); glCompileShader(v); glCompileShader(f); p = glCreateProgram(); glAttachShader(p,f); glAttachShader(p,v); glLinkProgram(p); glUseProgram(p); } int main(int argc, char **argv) { glutInit(&argc, argv); glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_DEPTH | GLUT_DOUBLE | GLUT_RGBA); glutInitWindowSize(512, 512); glutInitWindowPosition((glutGet(GLUT_SCREEN_WIDTH)-512)/2, (glutGet(GLUT_SCREEN_HEIGHT)-512)/2); glutCreateWindow("Use mouse to rotate"); trackball(cur, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0); glutDisplayFunc(display); glutReshapeFunc(reshape); glutMouseFunc(mouse); glutMotionFunc(motion); glutKeyboardFunc(processNormalKeys); glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST); glClearColor(1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0); glewInit(); if (!glewIsSupported("GL_VERSION_2_0")) { printf("GLSL not supported\n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } setShaders(); glutMainLoop(); return 0; }
Exercises #3
- Introduce zoom in/out functionality of the viewer by adding mouse wheel events to the end of
mouse()and introduction of global variableif (button == 3 && state == GLUT_DOWN) { zoom *= 1.1; glutPostRedisplay(); } else if (button == 4 && state == GLUT_DOWN) { zoom /= 1.1; glutPostRedisplay(); }
float zoom = 1.0;that is communicated to GPU by additionaluniform float Zoom;in thevertex_shader[]. Last line is replaced byIn thegl_Position = gl_ProjectionMatrix * RotationMatrix \ * gl_ModelViewMatrix*vec4(Zoom*gl_Vertex.xyz, 1.0); \
display()we sendzoomto GPU before drawing theglutSolidTeapot()by addinglocation = glGetUniformLocation(p, "Zoom"); if (location >= 0) glUniform1f(location, zoom);
Attachments (24)
-
ex1-5.png (6.0 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Exercise #1.5
-
first.png (3.9 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Legacy sample
-
triangle.png (2.9 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
First GLSL example
-
OpenGL-pipeline.svg (19.7 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
OpenL pipeline
-
temperature.png (5.8 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Temperature varying field
-
teapot.png (6.2 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Famous Utah teapot from GLUT
-
trackball.h (3.2 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Header for trackball
-
trackball.c (8.9 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Virtual trackball source for interactivity
-
motorBike.obj.gz (3.6 MB) - added by 13 years ago.
Example mesh from OpenFOAM tutorials/incompressible/simpleFoam/motorBike/constant/triSurface
-
motorBike-subset.png (66.4 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Complete motorBike mesh in VisIt
-
motorBike.obj (10.2 MB) - added by 13 years ago.
Example mesh from OpenFOAM tutorials/incompressible/simpleFoam/motorBike/constant/triSurface
-
motorBike.stl.bz2 (9.4 MB) - added by 13 years ago.
STL example from 1.7.1/run/tutorials/incompressible/simpleFoam/motorBike/constant/triSurface
-
copper-mix.png (30.7 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Copper mix Gouraud shading of the Teapot
-
point-cloud.png (26.7 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Point cloud from single vertex array
-
helmet.obj (303.4 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Rider's helmet with center at (0.5, 0, 1.2)
-
temperature.c (5.2 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Exercise 2.2
-
teapot.c (4.7 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Extended teapot example
-
wavefront.c (1.9 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Wavefront converter
-
motorbike-shadow.png (28.2 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Garbled normals on some parts of motorbike
-
motorbike-final.png (13.1 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Tooned motorbike example
-
motorbike.c (8.0 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Final motorbike source
-
p_yNormal.vtk (1.7 MB) - added by 13 years ago.
motorBike VTK data for pressure at cutting plane at time 500
-
pressure.png (22.3 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Pressure from p_yNormal.vtk
-
pressure.c (6.7 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Pressure example


